Top 10 SAP Vulnerabilities in 2020 Ranked by CVSS Score
CVSS Scoring
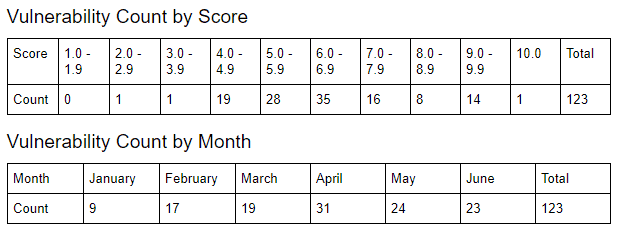
As covered in our recent blog, CVSS is a scoring system used to assign a value to a vulnerability. CVSS takes into account more than just the potential impact of a vulnerability, but also the ease of the exploit as well as a few other factors. For example, if there are two otherwise equal vulnerabilities that allow for root access to a system, but one requires physical access to the target while the other is remotely exploitable with network access, the remote exploit is considered more severe as this is easier to exploit. Scores range anywhere from 1.0 through 10.0. For a closer look at CVSS, have a read through our previous post.
A Quick Look at SAP Vulnerabilities in the First Half of 2020
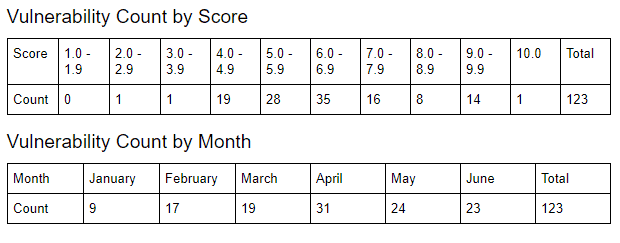
Between January and June 2020, there were a total of 123 vulnerabilities disclosed by SAP ranging from CVSS scores of 2.7 through 10.0. A total of 88 SAP components were affected.
The Top 10 List
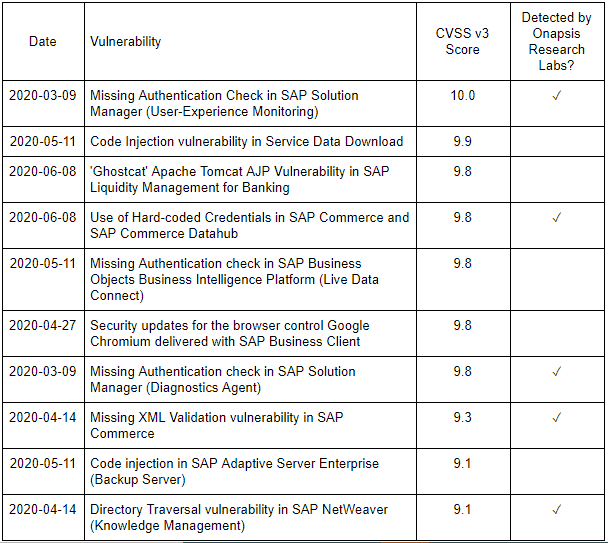
Below are the 10 top-scoring vulnerabilities from the first half of 2020. Of those, half were detected by Onapsis Research Labs, including the most severe.
The Vulnerabilities
#10 Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver
SAP Security Note: 2896682
CVE: CVE-2020-6225
CVSS Score: 9.1
Affected Component: SAP NetWeaver (Knowledge Management)
Summary: This is the second patch developed by SAP with the help of Onapsis Research Labs. The underlying vulnerability allows for path traversal in SAP NetWeaver Knowledge Management, which is a centralized access point for distributed repositories of files along the systems. It allows users to navigate through folders, create and delete files, etc. Among these functionalities is the ability for a user to upload files.
If Unpatched: The system does not sufficiently validate input and therefore may allow a potential attacker to overwrite, delete or corrupt arbitrary files on the remote server.
#9 Code Injection in SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise
SAP Security Note: 2917275
CVE: CVE-2020-6248
CVSS Score: 9.1
Affected Component: SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (Backup Server)
Summary: The SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE) Backup Server does not perform proper authentication checks for a user during ‘DUMP’ or ‘LOAD’ commands.
If Unpatched: If exploited, this allows for arbitrary code execution or Code Injection.
#8 Missing XML Validation Vulnerability in SAP Commerce
SAP Security Note: 2904480
CVE: CVE-2020-6238
CVSS Score: 9.3
Affected Component: SAP Commerce / SAP Hybris
Summary: SAP Hybris is an eCommerce Java-based platform providing solutions for B2B and B2C commerce, among others. This vulnerability is present in SAP Hybris with a default configuration and exploitable by a remote unauthenticated attacker. SAP provided patches for both SAP Hybris on-premises, as well as SAP Commerce Cloud.
If Unpatched: A malicious agent could read sensitive files and data from the system and, in limited scenarios, impact availability.
#7 Missing Authentication Check in SAP Solution Manager
SAP Security Note: 2845377
CVE: CVE-2020-6198
CVSS Score: 9.8
Affected Component: SAP Solution Manager (Diagnostics Agent)
Summary: This patch is part of a series of related vulnerabilities reported by Onapsis researcher, Yvan Genuer, that SAP began patching in July, 2019. This patch fixes the most critical vulnerability of the series, where a vulnerability in SMDAgent allows an attacker to bypass authentication and perform sensitive actions within the Diagnostics Agent.
If Unpatched: By exploiting this vulnerability, an attacker can bypass authentication. This means the attack can be executed by any person with access to the network, without the need of a valid user in the SolMan system. SMDAgent is a technical component which does not directly handle sensitive data of the business. However, this vulnerability allows an attacker to perform sensitive actions, such as stopping the system (availability), changing the behaviors of the application (integrity) or accessing sensitive information.
#6 Security Updates for the Browser Control Google Chromium Delivered With SAP Business Client
SAP Security Note: 2622660
CVE: N/A
CVSS Score: 9.8
Affected Component: Browser Control (Google Chromium) within SAP Business Client
Summary: This patch addresses a number of vulnerabilities in the 3rd party web browser control Chromium, which can be used within the SAP Business Client. Starting with SAP Business Client 6.5 PL5 and onward, there is an option to use Chromium as the browser control for displaying HTML content within the SAP Business Client. Depending on the browser control used, this may bring with it vulnerabilities and other security issues related to that browser, in this case, Chromium. Updates to the SAP Business Client, carry with it, security and stability updates for browser controls. More information on Chromium Security policy here.
If Unpatched: Successful exploits may result in information disclosure, a system crash (availability), and exfiltration of sensitive data. Information collected during an attack can be used to launch more sophisticated attacks in the future.
#5 Missing Authentication Check-in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform
SAP Security Note: 2885244
CVE: CVE-2020-6242
CVSS Score: 9.8
Affected Component: Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (Live Data Connect)
Summary: SAML authentication leverages digital certificates as part of the user authentication process. This vulnerability is the result of the certificate not protecting the Business Intelligence Platform, allowing for passwordless login to the Central Management Console.
If Unpatched: With access to the Central Management Console, an adversary could read, modify or delete sensitive information, access privileged administrative areas and potentially crash the service disrupting availability.
#4 Use of Hard-Coded Credentials in SAP Commerce & SAP Commerce Datahub
SAP Security Note: 2918924
CVE: CVE-2020-6265
CVSS Score: 9.8
Affected Component: SAP Commerce & SAP Commerce Data Hub
Summary: This problem is unfortunately found in many software products as they often use built-in accounts with publicly known passwords and do not force the administrators to change these passwords during or after installation. For example, every SAP Basis person knows the owners of “6071992” or “admin” passwords. After applying the patch, a new installation of SAP Commerce will only activate the built-in “admin” account. The installer is forced to maintain an initial password for that account. Other built-in users are still created during installation, but they are inactive until an individual password is set for these accounts. The later rule also applies to all built-in users of SAP Commerce Data Hub.
Important Note: This patch does not remove default passwords from built-in accounts on existing installations. As one option to achieve this, the note proposes to re-initialize the SAP Commerce installation after applying the patch, an option that likely does not apply to most customers. Therefore, the note also provides a Disabling All Default Passwords for Users Guide to remove the default passwords from all built-in accounts.
If Unpatched: An attacker that knows the default credentials could leverage these to login unnoticed, therefore exposing resources or functionality to unintended users and potentially allowing an attacker to execute arbitrary code.
#3 ‘Ghostcat’ Apache Tomcat AJP Vulnerability in SAP Liquidity Management for Banking
SAP Security Note: 2928570
CVE: CVE-2020-1938
CVSS Score: 9.8
Affected Component: Apache Tomcat (in SAP Liquidity Management)
Summary: Due to a known vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, called “Ghostcat,” SAP strongly recommends disabling all ports using the Apache JServ Protocol (AJP Protocol). If customers absolutely need the AJP protocol in their scenario, the note recommends setting the required secret attribute in the configuration of the AJP connector.
If Unpatched: At the very least, remote code execution, however, the SAP Note points out that “AJP connections…can be exploited in ways that may be surprising.”
#2 Code Injection Vulnerability in Service Data Download
SAP Security Note: 2835979
CVE: CVE-2020-6262
CVSS Score: 9.9
Affected Component: Service Data Download (Solution Manager Plugin)
Summary: Due to insufficient input validation in a remote-enabled function module that dynamically generates code, an attacker can take complete control of any SAP NetWeaver ABAP system that is connected to a Solution Manager (SolMan) system. Only the fact that an attacker needs a minimum level of authorizations to exploit this vulnerability has prevented it from receiving a CVSS of 10.0.
If Unpatched: A successful exploit of this vulnerability could result in unauthorized execution of commands, disclosure of confidential or sensitive information, and denial of service (availability).
#1 Missing Authentication Check in SAP Solution Manager
SAP Security Note: 2890213
CVE: CVE-2020-6207
CVSS Score: 10.0
Affected Component: Solution Manager
Summary: A critical bug reported by Onapsis Researchers (Pablo Artuso and Yvan Genuer). This vulnerability has been scored with CVSS 10.0, the highest value for this standard, since its vector includes low attack complexity (AC), no privileges required (PR), changed scope (S) and high impact in Confidentiality (C), Integrity (I) and Availability (A), among others. If an SAP customer wants to fully utilize the capabilities of SolMan, they must install an application called Solution Manager Diagnostic Agent (SMDAgent) on each host where an SAP system is running. This agent manages communications, instance monitoring and diagnostic feedback to SolMan. The Onapsis Research team identified that in default configurations, an unauthenticated remote attacker could be able to execute operating system commands as the SMDAgent OS user on each satellite’s system and achieve full privileges on the associated SAP systems.
If Unpatched: Complete compromise of all SMDAgents connected to the Solution Manager, including the execution of operating system level commands on each satellite system.
Key Takeaways
Strictly from a CVSS severity point of view, over 10% of the 123 SAP vulnerabilities disclosed in the first half of 2020 were 9.0 and above. Vulnerabilities with high CVSS base scores typically means lower effort to exploit them, while the consequences are high.
Three of the top vulnerabilities affected either SolMan itself, a plugin or other component for it. Given that SolMan is a centralized management tool for all SAP and non-SAP systems within a landscape, the consequences of an exploit are far-reaching.
Vulnerabilities allowing for passwordless authentication or leveraging default credentials often prove problematic to detect as they use existing users within the SAP system. Depending on actions performed and the method of attack, the indicators of the exploit may not appear anomalous.
Looking ahead to the second half of 2020, we’re already starting it off with a new vulnerability dubbed RECON (Remotely Exploitable Code On NetWeaver), which carries the maximum CVSS score of 10.0 and a US CERT alert to go along with it.
The tricky nature of detecting some of these vulnerabilities, coupled with the potentially severe business impact of a successful exploit, more comprehensive protection is required to protect the core of your business. Request a complimentary Cyber Risk Assessment from Onapsis for insights on vulnerabilities and misconfigurations within your environment that are putting your organization at risk.

