SAP Security Notes December ‘18: High Priority Missing Authorization Check Affecting SAP S/4HANA
Today, on SAP’s Security Patch Day, the company published 17 security notes, including a few that had been published during the month after the last Patch Day. Two notes tagged as Hot News and three tagged as High Priority excel over the rest, including a recurrent re-released note about Chromium (#2622660), a bug in SAP Hybris (#2711425) and a critical missing authorization check previously reported by the Onapsis Research Labs affecting most SAP users (#2698996). This last note affects not only SAP Netweaver ABAP systems, but also S/4HANA environments.
Why is a common vulnerability, such as a missing authorization check, sometimes considered as Low Priority and sometimes High Priority? Some of our readers may be confused about such gap in the way SAP tags one of the most common types of bugs and have asked us to explain. The note, reported this month by our lead researcher Matias Sena, is a good example to explain this. SAP Security Note #2698996, titled “[CVE-2018-2494] Missing Authorization Check in SAP Customizing Tools” was tagged as a High Priority note, based on what an alleged attacker can do if successfully exploited and its calculated CVSS 8.3 score reported by our team.
Authorization Checks are the way SAP programs protect what users can or cannot execute to access business sensitive data. If a program is properly developed, let’s say ‘in a secure way’, every time a user wants to access any function, program or transaction (among others), an authorization check should be executed in order to validate if this user should be allowed to do this (or not). Whenever a program lacks this check, it is called a Missing Authorization Check, since it may lead to an unauthorized user accessing or modifying data that shouldn’t be allowed. Based on this, the object that lacks the check allows a key to determine how risky a bug it is. For example, SAP Security Note #2463354 “Missing Authorization Check in the ABAP Workbench tools,” published in 2017, is tagged as Low Priority. If not patched, the affected component may allow an unauthorized user to create restricted data. Based on this, only integrity from Information Security Triage is not as affected and the bug CVSS vector is low (2.7/10). Whenever the affected component allows an unauthorized user to affect all CIA triage, the attack scenario is bigger, even though the type of bug is the same. This leads to a higher priority note. Whenever this vulnerability affects a component that almost every SAP customer in the world has enabled, it’s even worse. This is the case for SAP Security Note #2698996 published this month and reported by Onapsis Research Labs.
[CVE-2018-2494] Missing Authorization Check in SAP Customizing Tools
SAP Security Note #2698996, tagged as High Priority, fixes three vulnerabilities reported by the Onapsis Research Labs. The security bugs, consisting of a Missing Authorization Check were found by Onapsis researcher Matías Sena. The failed code affects both SAP Netweaver ABAP and S4/HANA systems. These systems share a lot of ABAP code, and as in this case, the same bugs. The problem is that several functions are used to customize different types of RFC connections, but not all the types. This security note has a CVSS 3 score of 8.3/10.
The reason this vulnerability is critical is because an attacker who has only network access to SAP servers and regular user credentials may perform system customizations that are usually reserved for SAP BASIS administrators.
This vulnerability allows an attacker to remotely manage certain types of RFC connections. It can enumerate, create, modify, activate or delete those RFC connections subject to the vulnerability. The affected RFC connections are: type L (Logical Destinations), type 3 (ABAP systems), type H ( HTTP Connection to an ABAP System), and, with less impact, type T (TCP/IP connections).
For each type, the possible actions for an attacker are almost the same (but the potential business impact may increase). For example, by just enumerating the RFC connections and its configurations, an attacker can gather information about the connections between SAP systems, that can be used in a further attack (well known as the reconnaissance stage of a cyberattack).
Another scenario could be the deletion or modification of one or more RFC Connections to disrupt the communications between different systems. Among the imaginable malicious goal of such an attack, one can consider, for example, the communications interruption of a monitoring/management system such as SAP Solution Manager or SAP GRC. This would keep it from functioning normally, because those systems cannot connect to monitor or manage their managed SAP systems within the organization. This kind of action could be used to hide another attack in progress, a common attacker tactic against supervised systems.
What else can be done? By changing an RFC destination in the Transport Management System, an attacker could potentially provoke a piece of modified code to pass from a Development to a Production system directly instead of following the regular steps of a QA/Testing system approval process.
Finally, in a worst-case scenario, exploitation of this bug could be used to potentially arrange a Man in the Middle (MitM) attack in an SAP environment. The attacker could take advantage of the vulnerability by changing an RFC destination from a legit SAP system to its own malicious server where the diverted information flow is subject to manipulation like data exfiltration or for malicious changes that can lead to fraud.
We strongly recommend patching this vulnerability as soon as possible, and checking whether the more strict authorization requirements for managing RFC destination are already in place only for the users that need it. This is the authorization for S_RFC_ADM as Solution section of the security note details.
Vulnerabilities in SAP Mobile Secure Android Client
The second security note for this month (#2707024) addresses a pair of vulnerabilities reported by Onapsis. It comes with fixes for two security bugs found in SAP Mobile Secure Android client, previously known as SAP Afaria Android client. This bug was also discovered by Onapsis researcher Yvan Genuer, as the one reported in last month’s blog.
In this note, the two vulnerabilities are because of lack of permissions required in some content provider functions in this Secure Android client. One vulnerability is allowing a non-privileged malicious app to write arbitrary content to the SAP Mobile Secure debugging log, allowing the attacker to hide its actions and consume disk space. The resulting impact is reduced and so is the CVSS score. Onapsis had designated this as a 4, but SAP estimated it to be 2.9. In an unpatched mobile, this could be helpful for the attacker to hide his actions when exploiting others vulnerabilities.
The other vulnerable function is also accessible to a non-privileged malicious app running in the same device. It can be abused to read and modify some configuration files of the Mobile Secure App. That way an attacker can access some configuration information files for the vulnerable app and exfiltrate it for further attacks. It can also manage to modify part of that configuration that can change the behavior of this SAP Mobile Secure app.
You should patch every mobile system and follow the solution provided by the security note and keep the software updated. The latest version for this Mobile-Secure.apl is the build 6.60.19942.0 SP28 1711.
Hot News and High Priority Notes
Two Hot News were issued today — one is for SAP Hybris Commerce. The note #2711425 addresses a Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability for it. SAP details that the affected versions of SAP Hybris Commerce are versions 6.2 through 6.7 and 18.08, including earlier and unsupported versions. All the storefronts based on non-updated Hybris Commerce versions are vulnerable.
SAP warns that also updated installations may remain vulnerable if they are running a storefront based on earlier vulnerable versions of Hybris Commerce. The reason for this is that the problem, the vulnerability, is with the JavaScript file webApplicationInjector.js (or a copy of it) when used by storefronts. Our recommendation is to study carefully the note’s solution and familiarize yourself with the SAP Hybris updating procedure to update and get rid of this vulnerability. At a minimum, follow one of the provided workarounds. If you are affected, keep in mind the high impact of this security note and the easy of exploitation that this vulnerability has clearly shown by its CVSS Score (9.3) and Base Vector.
Another Hot News issued today is the re-released note #2622660for SAP Business Client. This note includes the fixes for 23 security issues in Chromium controls, used in this SAP client software. Six of those bugs are tagged as having a high impact. For example, one of them (CVE-2018-17463) allows an attacker, via a crafted HTML page, to run arbitrary code inside the sandbox (a mechanism to isolate browser processes). Most of the vulnerabilities fixed were externally reported. A prompt update to the newest SAP Business Client 6.5 PL11 is strongly recommended.
In addition to the High Priority note we already discussed above, there are two other High Priority notes and both are for SAP Netweaver AS Java. One of these is the #2642680 that fixes a Missing XML Validation in SAML 2.0. This SAML 2.0 adds a functionality to SAP AS Java allowing the integration between different authentication domains by the exchange of identity information with this version of the SAML standard used for exchanging authentication and authorization data between different systems. In this case, the integration between the enterprise SSO mechanism and the cloud-based service providers. The vulnerability allows an attacker to perform a Denial of Service attack and also to retrieve arbitrary files from the vulnerable server. The attack has a high impact on the availability and can be performed remotely and with low privileges from an untrusted source.
The second High Priority note affecting SAP Netweaver AS Java is a wrong default authorization in the AS Java keystore. The note #2658279 has directions for patching the affected server versions that are the following: 7.11, 7.20, 7.30, 7.31, 7.40 and 7.50. The Java keystore service allows storing certificates and keys such as used for credentials emails over SSL and store for Trusted CAs. The impact of this security bug will allow accessing sensitive information from the keystore that can be used to get access to protected resources or to cause a service disruption if a key or certificate were maliciously deleted or modified.
Summary and Conclusions
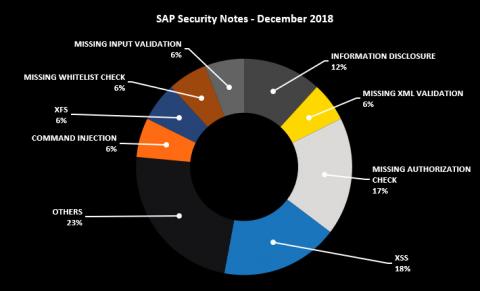
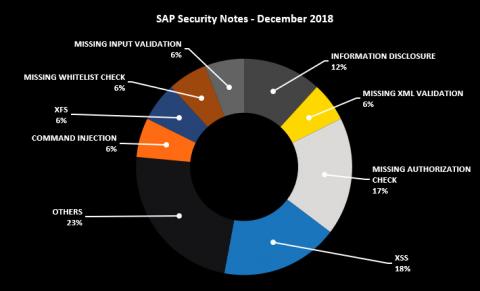
This month there are several relevant SAP Security Notes that, if not addressed, can have serious security implications, including a High Priority Note that affects most SAP customers. Below is a summary of the type of bugs SAP patched this month through its security notes:
SAP recognized Onapsis through two researchers from our Research Labs, Matías Sena and Yvan Genuer, who have helped SAP improve the security and integrity of their customers’ systems. As we regularly do at Onapsis, we are working to update the Onapsis Security Platform to incorporate these newly published vulnerabilities. This will allow our customers to check whether their systems are up to date with the latest SAP Security Notes and will ensure that those systems are configured with the appropriate level of security to meet their audit and compliance requirements.
Please follow our ERP security blog or follow us on Twitter for more information about the latest SAP security issues and stay tuned for our year-in-review blog post leading up to the first January Patch Day.
