SAP Security Patch Day April 2021: Serious Vulnerability Patched in SAP Commerce

Highlights of April SAP Security Notes analysis include:
- April Summary—23 new and updated SAP security patches released, including three HotNews notes and five High Priority notes
- Active Cyberattacks on SAP Applications—New threat intelligence report published by Onapsis and SAP
- Critical Patch released for SAP Commerce—Vulnerabilities in Rules Engine keeps administrators busy
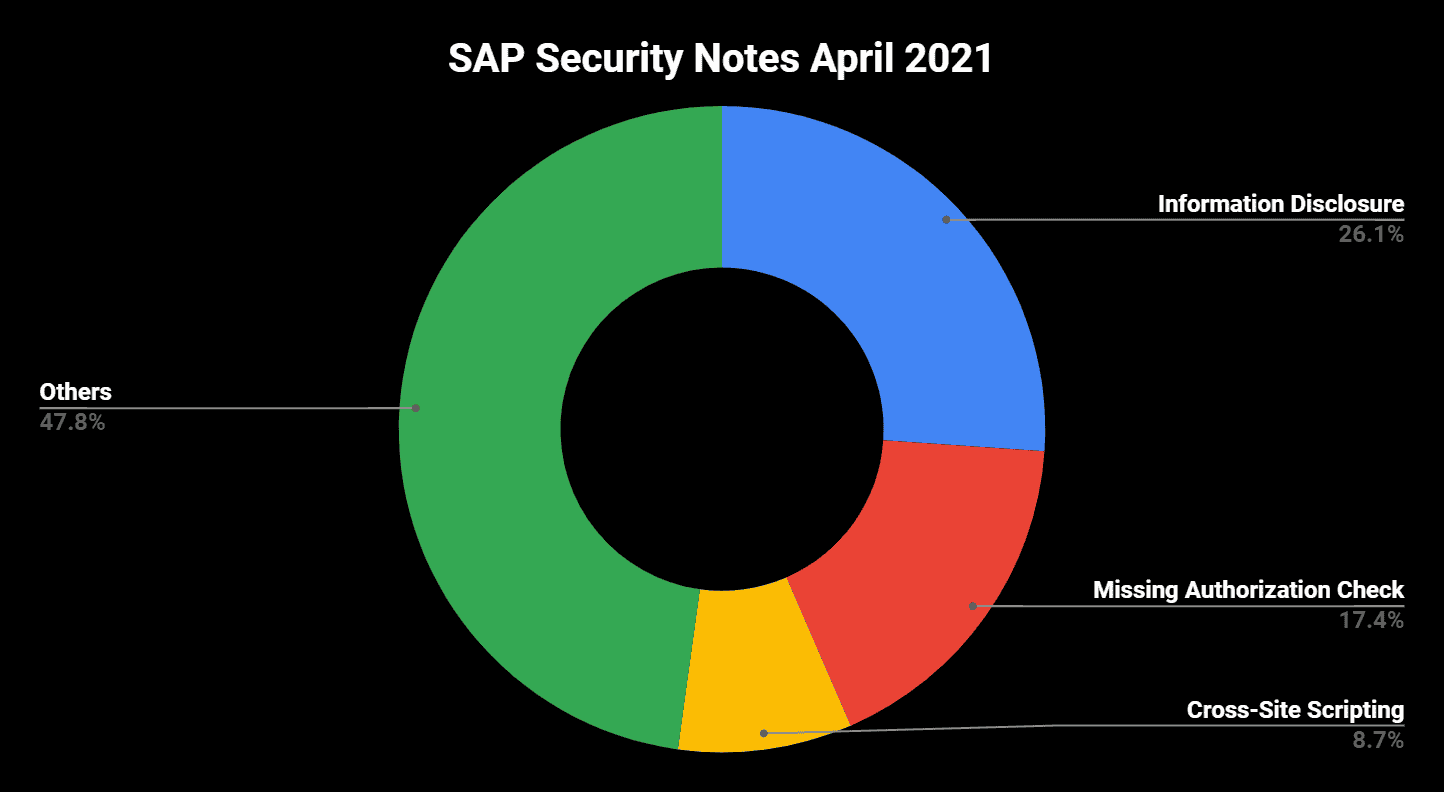
SAP has released 23 new and updated SAP Security Notes in its April 2021 patch release, including the notes that were released since last patch day. As part of this month’s patch release, there are three HotNews notes and five High Priority notes.
SAP Security Note #2622660, tagged with a CVSS score of 10 is the permanent patch day companion that comes with the newest SAP Business Client Patch including Google Chromium version 89.0.4389.90. The maximum CVSS score of all vulnerabilities that were fixed with this newest supported Chromium version, compared to the last one, is 9.6. This includes the patch of 62 vulnerabilities in total with 25 of them rated as High Priority.
HotNews note #3022422, tagged with a CVSS score of 9.6 was originally released in March’s patch day and just contains an update to an FAQ link. This might help customers who did not yet apply the patch after it was released last month in order to get detailed information about the patch and its impact.
One of the five High Priority Notes, SAP Security Note #2993132, tagged with a CVSS score of 7.6 was originally released in December 2020 and just contains updates on the included correction instructions. The note patches a Missing Authorization Check vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP and SAP S4 HANA (SAP Landscape Transformation).
In Focus: Threat Intelligence Report published by Onapsis and SAP
On April 6, Onapsis and SAP released a new threat intelligence report to help SAP customers protect their organizations from active cyber threats seeking to specifically target, identify and compromise organizations running unprotected SAP applications, through a variety of cyberattack vectors.
In this report, the Onapsis Research Labs share observations and cybersecurity intelligence that reveal a complex threat landscape targeting mission-critical SAP applications. From mid-2020 until publication of this report, Onapsis researchers have recorded more than 300 successful exploit attempts on unprotected SAP instances. This significant exploit activity was related to multiple vulnerabilities (CVEs) and insecure configurations.
During this time, the Onapsis Research Labs captured thousands of exploitation events, including both automated and hands-on-keyboard, from a wide variety of sources. The observed activity is mostly related to six CVEs and one critical configuration issue, all being known vulnerabilities. While SAP issues monthly patches and provides best practices for configuring systems, it is ultimately the responsibility of the customer or their service provider to apply mitigations in a timely manner and properly configure systems to keep critical business processes and data protected and in compliance. All observed exploited critical weaknesses have been promptly patched by SAP, and have been available to customers for months and years in some cases. Unfortunately, both SAP and Onapsis continue to observe many organizations that have still not applied the proper mitigations mentioned in this report, allowing unprotected SAP systems to continue to operate and, in many cases, remain visible to attackers via the internet.
The evidence clearly shows that cyber criminals are actively targeting and exploiting unprotected SAP applications with automated and sophisticated attacks. This research also validates that the threat actors have both the means and expertise to identify and exploit unprotected SAP systems and are highly motivated to do so. Onapsis researchers found reconnaissance, initial access, persistence, privilege escalation, evasion and command and control of SAP systems, including financial, human capital management and supply chain applications.
Beyond malicious activity targeting unpatched SAP applications, Onapsis researchers also observed evidence of attacks against known weaknesses in application-specific security configurations, including brute-forcing of high-privilege SAP user accounts. Additionally, attempts at chaining vulnerabilities to achieve privilege escalation for OS-level access were observed, expanding potential impact beyond SAP systems and applications.
Key Findings
-
Threat actors are active, capable and widespread—Evidence of 300+ automated exploitations leveraging seven SAP-specific attack vectors and 100+ hands-on-keyboard sessions from a wide range of threat actors. Clear evidence of sophisticated domain knowledge, including the implementation of SAP patches post-compromise.
-
The window for defenders is small—Critical SAP vulnerabilities being weaponized in less than 72 hours of a patch release and new unprotected SAP applications provisioned in cloud (IaaS) environments being discovered and compromised in less than three hours.
- Threats have both security and compliance impact—Exploitation would lead to full control of unsecured SAP applications, bypassing common security and compliance controls, enabling attackers to steal sensitive information, perform financial fraud or disrupt mission-critical business processes by deploying ransomware or stopping operations. Threats may also have significant regulatory compliance implications, including SOX, GDPR, CCPA and others.
The complete threat intelligence report can be downloaded here.
Critical SAP Security Notes in April
Similar to SAP’s February Patch Day, the only HotNews note besides the regularly recurring SAP Business Client note #2622660 and the minor update of HotNews #3022422 note, fixes a vulnerability in the Rules Engine of SAP Commerce. SAP Security Note #3040210, tagged with a CVSS score of 9.9 describes that certain authorized users of the SAP Commerce Backoffice application can exploit the scripting capabilities of the Rules engine to inject malicious code in the source rules. This can lead to a remote code execution with critical impact on the system’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The released patch introduces additional validations and output encoding when processing rules. More details on the architecture of the SAP Commerce Rules Engine can be found here.
High Priority note #3017908 is tagged with a CVSS score of 8.3 and patches an Information Disclosure vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver Master Data Management (MDM). The fact that administrative accounts in MDM were not locked after a defined number of unsuccessful connection retries enabled attackers to start brute force attacks. As a workaround but also as an additional security level after the patch has been implemented, SAP recommends to update the relevant password parameters to values that enforces a strong password policy.
Another Information Disclosure vulnerability affects SAP Solution Manager (SolMan). SAP Security Note #3017823, tagged with a CVSS score of 8.1 patches the vulnerable function module that allowed high privileged attackers to get access to sensitive data. The complete patch of the vulnerability also includes fixing issues in the LM-Service component. The corresponding patches are referenced in the note.
The vulnerability patched with High Priority note #3039649 and tagged with a CVSS score of 7.5 puts user workstations at risk. It affects the SAPSetup tool that supports the software distribution of SAP frontend products. An unquoted service path in SAPSetup could lead to privilege escalation during the installation process that is performed when an executable file is registered. While the impact on the workstation’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability can be very high, the complexity of an attack and the amount of privileges required leads to a CVSS score of “only” 7.5. SAP provides a corresponding update of the SAPSetup executable on its Support Portal.
A third critical Information Disclosure vulnerability is patched in SAP NetWeaver AS Java with SAP Security Note #3001824, tagged with a CVSS score of 7.4. This vulnerability is a direct result of a Server Message Block(SMB) Relay attack. An SMB attack is a kind of a Man-in-the-Middle attack that allows the attacker to capture password hashes. An unauthorized attacker could benefit from this option and trick an administrator into starting specific telnet commands for an SAP NetWeaver AS Java which would allow the attacker to gain NTLM hashes of privileged users. The provided solution as well as well as the optional workaround prevents the usage of the SMB protocol.
Summary and Conclusions
This month, the most important information was already released before the regular patch day. The results of the Onapsis and SAP threat intelligence report clearly demonstrate that there is not only a theoretical risk for SAP applications, but a real risk as well as attackers are now focusing their efforts on mission-critical SAP applications.
Continuous patching is one prerequisite for keeping the company’s most valuable data and processes protected. Therefore, we should not feel disturbed by each new patch day—we should approach it as another chance to make our systems secure.
As always, the Onapsis Research Labs is continuously updating The Onapsis Platform to incorporate the newly published vulnerabilities into the product so that our customers can protect their businesses.
For more information about the latest SAP security issues and our continuous efforts to share knowledge with the security community, subscribe to our monthly Defender’s Digest Onapsis Newsletter.
