SAP Security Patch Day October 2020: SAP Solution Manager and SAP Focused Run Affected by Two Critical Vulnerabilities

Highlights of October SAP Security Notes analysis include:
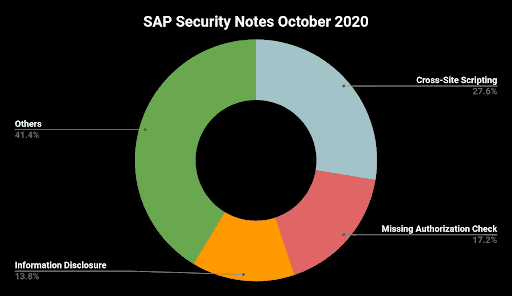
- October Summary—29 new and updated SAP security patches released, including two HotNews Notes and seven High Priority Notes
- CA Introscope Enterprise Manager—Onapsis Research Labs detected two critical vulnerabilities that affects Solution Manager and Focused Run
- Cross-Site Scripting—More than 25% of all patches fixes a Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability
SAP has published 29 new and updated Security Notes on its October patch day. This number includes two HotNews Notes and seven High Priority Notes.
The most affected component of this patch day is CA Introscope Enterprise Manager. The Onapsis Research Labs has detected two serious vulnerabilities in this optional software component that is used to monitor non-ABAP applications and infrastructures in an SAP landscape, including one HotNews note with a CVSS Score of 10. Considering these two new corresponding patches, Onapsis has helped SAP to fix three HotNews vulnerabilities with a CVSS score of 10 as well as nine other HotNews and 13 High Priority vulnerabilities in total during 2020. The expertise of the Onapsis Research team,which is continuously integrated into the Onapsis Platform, was one of the reasons whySAP invited Onapsis and our leading solution for mission-critical application cybersecurity and compliance into its Endorsed Apps Program. More details can be found here. As we do every month, let’s analyze the most critical SAP Security Notes with further details.
In Focus: CA Introscope Enterprise Manager
CA Introscope Enterprise Manager is part of CA APM Introscope(R), an application performance management solution to manage Java Application performance. With the Right to View (RTV) version of CA APM Introscope, SAP ships a read-only version of the full product that is bundled with SAP Solution Manager (SolMan). This version only supports products that are licensed and supported by SAP. CA APM Introscope is integrated in the SolMan infrastructure. While the CA Introscope Enterprise Manager(s) are directly connected to SolMan, the Introscope Host Adapters (also known as Wily Host agents) are running inside the SolMan Diagnostics agents (SMD agents) that are installed on each SAP host that is monitored by SolMan.
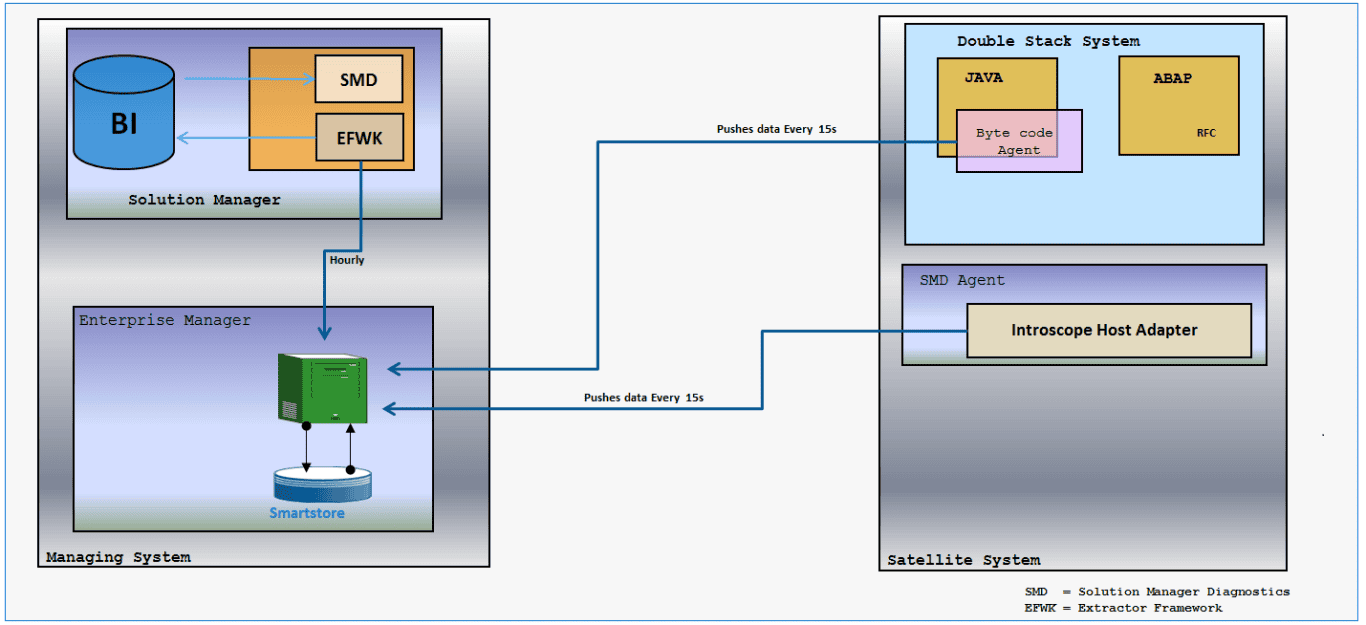
The Onapsis Research Labs found two critical vulnerabilities in the application. The first one is an OS command injection vulnerability that is patched with SAP HotNews Security Note #2969828. This note is the third one in 2020 that has assigned a CVSS score of 10. It affects all CA Introscope Enterprise Manager versions with release 10.7.0.304 or lower. The vulnerability can allow an attacker to inject OS commands and thus gain complete control of the host running the CA Introscope Enterprise Manager. The CVSS score of 10 considers the fact that an exploit can be started remotely and does not require authentication orany privileges.
The preferred solution provided by SAP is to patch Introscope Enterprise Manager to the highest patch level of Enterprise Manager 10.7.
Customers on Enterprise Manager 10.5 have two options:
- There is a patch available for Enterprise Manager 10.5.2.113. Customers on versions < 10.5.2.113 have to patch to version 10.5.2.113 before they can apply the 10.5 patch
- 10.5 customers can also directly patch to 10.7.
Advantages of option 2)
- The upgrade to 10.5.2.113 effort is mainly the same as upgrading to 10.7
- 10.5 is running out of maintenance in December 2020 anyway
- SolMan support for 10.7 is broader than for 10.5
Possible disadvantage of option 2)
- Enterprise Manager 10.7 requires Solution Manager 7.2, SP05 and higher!
The second vulnerability, detected by the Onapsis Research Labs, is patched with High Priority Note #2971638, tagged with a CVSS score of 7.5. It allows a remote attacker to bypass authentication if the default passwords for Admin and Guest have not been changed.
Referring to the SAP Security Note, customers are safe if they change the default passwords of the two standard users. Nevertheless SAP’s mission is to deliver “Security by Default” and thus, the note provides a patch solution with very similar options as note #2969828:
If Enterprise Manager is updated to 10.7 SP0 Patch 2 or higher (the recommended approach for customers on versions < 10.5), no explicit patch is required.
But remember:
Enterprise Manager 10.7 requires SolutionManager 7.2, SP05 and higher!
There is the same patch available for Enterprise Manager 10.5 versions and 10.7 versions < SP0 Patch 2.
After patching, customers with default passwords are forced to set new credentials for Enterprise Manager. Furthermore, the connection between SAP Solution Manager/Focused Run and Introscope must be restored manually. For details, refer to the SAP Security Note.
Other Critical SAP Security Notes in October
The second HotNews Note is the well-known SAP Security Note #2622660, announcing another update of the Chromium version that is shipped with SAP Business Client patch. This update patches 25 security issues, seven of them with High Priority.
In addition to High Priority Note #2971638, described in the previous section, SAP has released two new High Priority Notes.
SAP Security Note #2972661, tagged with a CVSS score of 8.1, patches a Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in the SAP NetWeaver Composite Application Framework. It allows an unauthenticated attacker to trick an unsuspecting authenticated user to click on a malicious link.
The end user’s browser has no way to know that the script should not be trusted, and will execute the script, resulting in sensitive information being disclosed or modified.
SAP Security Note #2969457, tagged with a CVSS score of 7.6, affects the “Compare Systems” tool of SAP NetWeaver AS Java. A missing XML validation allows an attacker with administrative privileges to retrieve arbitrary files from the OS level of the application server and/or to start a denial-of-service attack.
The remaining four High Priority Notes are just updates and have been initially released on former patch days. Nevertheless, while such updates often contain only textual extensions and adjustments, this time it is worth to re-read them as they contain additional patches compared
to their initial version. This affects:
- SAP Security Note #2941667: “Code Injection Vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver (ABAP) and ABAP Platform”
- SAP Security Note #2941315: “Missing Authentication check in SAP NetWeaver AS JAVA”
- SAP Security Note #2898077: “Information Disclosure in SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence Platform (dswsbobje Web Application)”
- SAP Security Note #2902456: “Privilege Escalation in SAP Landscape Management (SAP Adaptive Extensions)”
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerabilities
In every month’s SAP patch release day, Cross-Site Scripting is one of the most patched vulnerability types. Among others, the possible impact of an XSS attack can be:
- Carry out any action that the user is able to perform
- Capture the user’s login credentials
- Inject trojan functionality into the web site
What is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)?
Cross-Site Scripting (also known as XSS) is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to compromise the interactions that users have with a vulnerable application. It allows an attacker to circumvent the same origin policy, which is designed to segregate different websites from each other. XSS vulnerabilities normally allow an attacker to masquerade as a victim user, to carry out any actions that the user is able to perform, and to access any of the user’s data. If the victim user has privileged access within the application, then the attacker might be able to gain full control over all of the application’s functionality and data.
How Does XSS Work?
Cross-Site Scripting works by manipulating a vulnerable website so that it returns malicious JavaScript code to users. When the malicious code executes inside a victim’s browser, the attacker can fully compromise their interaction with the application.
Depending on the origin of the malicious JavaScript, there are three different types of XSS attacks:
- Reflected XSS: the malicious script comes from the current HTTP request
- Stored XSS: the malicious script comes from the website’s database
- DOM-based XSS: the vulnerability exists in client-side code rather than server-side code
Summary & Conclusions
With 29 new and updated SAP Security Notes, SAP’s October patch day is one of the “busy” patch days of 2020. Even the updated notes should be studied carefully as they contain substantial extensions and improvements.
With CA Introscope Enterprise Manager, a 3rd party application is in focus of SAP’s October patch day. Considering that SAP customers normally have multiple 3rd party applications in place—most of them typically ABAP applications—it is always important to include security aspects when deciding for a specific application. The Onapsis Platform supports SAP customers in automating the quality assurance process when testing external applications for code security, code robustness and code maintainability as well as for transport security.
As always, the Onapsis Research Labs is already updating The Onapsis Platform to incorporate the newly published vulnerabilities into the product so that our customers can protect their businesses.
For more information about the latest SAP security issues and our continuous efforts to share knowledge with the security community, subscribe to our monthly Defender’s Digest Onapsis Newsletter.